When and how to start coding with kids
Episode Deep Dive
1. Why Teach Kids to Code?
- Reasons and Benefits
- Encourages computational thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Fosters creativity by allowing kids to build games, stories, and more.
- Develops perseverance—kids learn to iterate on challenges and overcome obstacles.
2. Development Stages for Teaching Programming
Ages 0 to 4
- Very early stage: kids develop motor and vision skills; not ready for complex coding concepts.
- Focus on playful, screen-free exploration and simple problem-solving (e.g., breaking down tasks like guiding a toy through a maze).
Ages 4 to 6
Can begin exploring basic sequencing with physical toys that teach algorithmic ideas:
BeeBot (robot bee you program with directional buttons)
Robot Turtles (a board game that uses simple card commands for movement)
Ages 6 to 9
Greater focus on visual programming languages and simple robotics:
Scratch Jr. (tablet-based app, puzzle-piece style commands)
Cubelets (magnetic robotic cubes; can be used at slightly older ages too)
Ages 9 to 12
Kids can handle more complex visual tools and even basic text-based coding:
Scratch (full version for more advanced projects)
Blockly (Google’s foundational visual coding approach)
BBC micro:bit (affordable microcontroller; can code in MakeCode or Python)
Ages 10+ / 11+
Moving toward textual programming (Python, etc.) and more robust hardware:
Zumi (self-driving car kit that supports Python or Blockly, plus machine learning)
Raspberry Pi (a full computer in a small board, great for learning Linux + Python)
3. Coding Tools and Platforms for Older Kids (Text-Based)
- Code Combat
- Game-based approach teaching Python or JavaScript in a fun RPG setting.
- Heavy autocomplete to reduce syntax errors and frustration.
- Code Club (Raspberry Pi Foundation)
- Offers structured lessons transitioning from Scratch to Python.
- codeclub.org/en (international versions available)
- Hedy
- Gradual programming approach based on Python.
- Starts with almost zero syntax requirements, then progressively adds complexity.
- Anvil
- Drag-and-drop web app builder that uses Python for both front-end and back-end logic.
- Simplifies the creation of real, shareable web apps.
- Adafruit & CircuitPython (Mentioned in the Hardware Context)
- Broad set of microcontroller boards and sensors for hands-on projects.
- adafruit.com (official store)
- circuitpython.org (CircuitPython details)
4. Practical Guidance for Parents and Educators
- Focus on Fun: Encourage play and experimentation, whether with board games, robots, or code challenges.
- Screen-Free Options: Especially for younger children (e.g., Robot Turtles, Cubelets in offline mode).
- Gradual Learning: Visual coding first, then move to textual coding as typing and problem-solving skills mature.
- Praise Persistence: Recognize effort, not just results, to build kids’ confidence and enjoyment.
- Follow Their Interest: If they love games, choose game-based coding; if they’re curious about robots, choose robotics kits.
Overall Takeaway
Teaching kids to code successfully involves matching age-appropriate tools with hands-on, playful experiences. By starting with robotics toys or block-based languages—then moving toward more sophisticated projects in Python or other text-based environments—kids gain computational thinking, problem-solving skills, and a love of learning that will serve them well into the future.
Links from the show
Magical universe repo: github.com
Machine learning basics repo: github.com
PyData recording "when and how to start coding with kids": youtube.com
Robots and devices
Bee Bot: terrapinlogo.com
Cubelets: modrobotics.com
BBC Microbit: microbit.org
RaspberryPi: raspberrypi.com
Adafruit Qualia ESP32 for CircuitPython: adafruit.com
Zumi: robolink.com
Board games
Think Fun Robot Turtles Board Game: amazon.com
Visual programming:
Scratch Jr.: scratchjr.org
Scratch: scratch.org
Blocky: google.com
Microbit's Make Code: microbit.org
Code Club: codeclubworld.org
Textual programming
Code Combat: codecombat.com
Hedy: hedycode.com
Anvil: anvil.works
Coding classes / summer camps (US)
Portland Community College Summer Teen Program: pcc.edu
Watch this episode on YouTube: youtube.com
Episode #478 deep-dive: talkpython.fm/478
Episode transcripts: talkpython.fm
---== Don't be a stranger ==---
YouTube: youtube.com/@talkpython
Bluesky: @talkpython.fm
Mastodon: @talkpython@fosstodon.org
X.com: @talkpython
Michael on Bluesky: @mkennedy.codes
Michael on Mastodon: @mkennedy@fosstodon.org
Michael on X.com: @mkennedy
Episode Transcript
Collapse transcript
00:00 Do you have kids? Maybe you have nieces or nephews? Or do you work in a school environment?
00:04 Maybe it's just friends who know you're a programmer and ask about how they should go
00:08 about introducing programming concepts to their kids. Anna-Lena Popkes is back on the show to
00:13 share her research on when and how to teach kids programming. We spend the second half of this
00:19 episode talking about concrete apps and toys you might consider for each age group. Plus,
00:25 some of these are fun for adults too. This is Talk Python To Me, episode 478, recorded August 8th,
00:33 2024. Welcome to Talk Python To Me, a weekly podcast on Python. This is your host, Michael Kennedy.
00:52 Follow me on Mastodon where I'm @mkennedy and follow the podcast using @talkpython,
00:58 both accounts over at fosstodon.org. And keep up with the show and listen to over nine years of
01:04 episodes at talkpython.fm. If you want to be part of our live episodes, you can find the live streams
01:09 over on YouTube. Subscribe to our YouTube channel over at talkpython.fm/youtube and get notified
01:15 about upcoming shows. This episode is brought to you by WorkOS. If you're building a B2B SaaS app,
01:22 at some point your customers will start asking for enterprise features like SAML authentication,
01:26 SKIM provisioning, audit logs, and fine-grained authorization. WorkOS helps ship enterprise
01:32 features on day one without slowing down your core product development. Find out more at
01:37 talkpython.fm/workos. And it's brought to you by us over at Talk Python Training. Did you know
01:45 that we have over 270 hours of Python courses? Yeah, that's right. Check them out at talkpython.fm
01:51 slash courses. Anna Lena, welcome back to Talk Python. It's awesome to have you here.
01:57 Yeah, thanks for having me again.
01:58 Yeah, it's always fun to have you on. You've got interesting and playful topics. I think the very
02:04 first time that you were on the show, I can't remember how many years ago, but it's been a little
02:08 while, was to talk about learning Python through Harry Potter. Is that right? In the magical universe.
02:13 Yeah, I still love that project a lot.
02:15 Yeah, people can find that on GitHub and they obviously can find that episode on talkpython.fm.
02:21 But we're back for, I would say, another playful episode in a sense, right? Continuing the theme. I'm going to talk about when should you teach kids to program? And maybe even more importantly, what are some age appropriate resources that spans a good chunk of what a kid's life is? You know, like a kid, not a kid at 18. I don't know. But lower than that, a lot of resources.
02:44 Exactly.
02:45 Yeah, so that's going to be a lot of fun. It has been a while since you've been on the show, though. So just a quick introduction about who you are and what you do for everyone listening.
02:52 Yeah, actually, not much has changed since the last episode. I think that was on Python packaging. I'm still a senior machine learning engineer at a German company called InnoVex, where I jump from project to project. I'm currently working at the speech recognition team at Bubble still. Was that last time as well? I'm not sure.
03:10 I think so. I believe so.
03:11 Yes. Yeah, I'm still there in the project. I love it. It's a very interesting topic. And yeah, I love Python. We have talked about different topics over the years. And this time it's on children. And talk I prepared for PyData and the PyCon here in Germany. And it was lots of fun to learn about it.
03:29 Yeah, it looks like you did a lot of research.
03:31 I did.
03:32 To go into this. And I think it's probably worth pointing out that we both are parents. And so we have some interest in this topics, you know, close to home as well. My kids are getting a little bit older for any of this kind of guidance. But still, you know, a lot of things I thought about as they were growing up. And some of these things we're going to talk about, I've actually used, you know, before I saw them on your list as well, which is cool. But yeah, it's a personal topic, I suppose.
03:57 Yeah, absolutely. For me, it's also personal, because I did not have any coding opportunities growing up myself. I really want this to be different for children growing up now and my own kids. That's also a reason why I wanted to do the research. So that would be just different.
04:12 Let me know what you think. I feel like there are social stigmas, like this person should be a coder, and that person shouldn't be a coder, they should go do something else. And that may or may not be around gender, but often it is, unfortunately. But when you're six years old, you don't care. You like games, you want to play a game, you want to explore things are interesting, right?
04:32 So I feel like this kind of stuff also has a big opportunity to short circuit these unnecessary influences, I guess, depending on different cultures.
04:41 And also just having it in your environment, if there's like a person in your family or your friend circle, or even at school, and you have some opportunity to learn about it, it helps a lot.
04:52 For me, it just wasn't a topic ever. And I still remember my parents, when I told them that I was switched to computer science in my graduate degree, they were like, are you sure you want to do that?
05:02 Isn't that like very nerdy, techie stuff? And I'm so happy I did the switch, even though it was quite hard in the beginning, but it's an amazing topic. And there's so much cool stuff to do. It's just not only the nerdy stuff.
05:16 It's always got something new. That's both the benefit and the curse of it. What you've learned is powerful and helpful, but there's more to learn.
05:22 Yeah, always. But that makes like keeps it interesting, right? You never get bored.
05:27 Exactly. Especially when JavaScript.
05:29 Okay, so I feel like as your parents had that thought, you know, probably one thing they may have thought, I know, obviously, I don't know them.
05:37 But a lot of people would think is that's a very antisocial sort of thing, right? Like, oh, you're going into programming, that means you're gonna sit behind a computer screen.
05:46 Completely alone and not talk to people. And I think that's one of the misconceptions of programming.
05:51 Yeah, absolutely. Even now, when I'm working remotely, most of the time, I have so many meetings and collaborations with other developers. And I don't ever feel not part of my team, even if I don't see them, because we interact so much.
06:05 Sometimes they sit on a completely different continent, and it still feels very close.
06:10 And we do love and we don't only pair code, but we like, yeah, you get to know them well.
06:16 And it's lots of fun, interesting people that are not the stereotype of coders at all.
06:23 Yeah, absolutely.
06:24 I bring that up because I think some people listening might be attracted to the show who don't necessarily work as programmers themselves, you know?
06:30 I can very, like, I can recommend it a lot. I think it's a lot of fun.
06:33 Absolutely.
06:34 All right. Well, we talked about some of the reasons that we're interested in this, obviously.
06:40 But why? I mean, as people who like programming, we may want to communicate or share that thing we like with other kids, with our kids and so on.
06:50 But I think programming also can stand in for a lot of more traditional things, such as, like, geometry and so on.
06:57 Yeah, I think what I like most about it is that you can really make things.
07:01 You can see them come alive and it can be a game.
07:04 It can be something more math related.
07:07 It can be music, websites.
07:09 You can just create anything that you're interested in and even have so much fun seeing it come to life.
07:15 So it's not just learning a skill, maybe for a job or your life at home or your hobbies, but it's more of like being able to create anything that you're interested in.
07:26 And then, of course, you have the obvious advantages like the career opportunities and lots of skills that are taught by learning how to code that you do not think about in the beginning, I guess.
07:37 Yeah, absolutely.
07:38 The realism or I've created something I can see, even though it's still digital and virtual and you can't actually touch it usually unless it's like robotic or something.
07:46 But that's so much more realistic and interactive than things like, oh, you're going to learn these axioms and then we're going to teach you how to, you know, prove stuff about angles and triangles with these axioms.
07:59 It's going to teach you logical thinking.
08:01 So, you know, sit down for the year and we're going to talk about small angles, big angles, diagonal, cross connected, all that kind of stuff.
08:09 Right.
08:09 Which is a little bit useful, but being able to work with computers is way more.
08:13 And I think it teaches these problem solving and computational thinking skills at least as well.
08:19 Yeah, absolutely.
08:20 Especially what you said, like problem solving, logical thinking that kids, like not only adults, but kids especially, they understand that you have might have a complex problem you want to solve, but you can break it down into simpler steps.
08:32 Like what an algorithm is actually doing, giving you a step by step path to reaching a goal.
08:38 You can teach that not only by coding, also, of course, by just playing and seeing you want to build this huge Lego piece, but you start building it with little pieces and put it all together.
08:50 And that's also what you have in coding.
08:51 You want to reach a goal.
08:52 You want to program a game or maybe create an animation and you understand how to break it down.
08:58 It helps us or also kids to make more structured decisions.
09:02 I think that's a very valuable skill to learn, not only for coding, but for everyday life, I guess.
09:07 You want to break problems down and solve them.
09:08 It helps.
09:09 That's like adulthood right there.
09:10 What I also find really helpful is one of the skills I looked at specifically is perseverance.
09:16 Also for kids, they get frustrated so easily.
09:19 And give up and say like, this is not working.
09:22 I don't like this.
09:22 Like, I hate this.
09:23 And start throwing their toys around.
09:25 At least we are at this stage.
09:27 Your kids are probably not doing that anymore.
09:30 But yeah, I think with coding, when you encourage them to keep going, even or especially when they fail, that they understand that failure isn't something bad,
09:40 but rather it keeps you improving.
09:42 It keeps you going and that you can learn to see challenges or problems at something positive
09:49 and something you can grow with.
09:51 I think that's really, really great about coding because you will have that a lot when you learn
09:56 how to code.
09:57 Yeah, I absolutely agree with you.
09:58 In the problem, this perseverance skill is incredibly important.
10:02 I agree.
10:03 It manifests itself a little bit differently as they get older.
10:06 Instead of going, I dislike this, you know, like these are those toys crap.
10:10 I can't make it do its thing or whatever.
10:12 It's more, I can't do this.
10:14 I'm not good at this.
10:15 And a really important skill, I think, is not, I can't do this.
10:20 Like, I need to work at being good at this.
10:23 And that perseverance that you learn.
10:25 Honestly, I think one of the very most important skills that people can have as a programmer
10:29 or in software development in general is perseverance.
10:33 Like, it doesn't work.
10:34 I read the docs.
10:35 It still doesn't work.
10:36 I read Stack Overflow.
10:37 People were mean.
10:38 Still didn't help me.
10:39 But eventually, I worked my way and now it works.
10:42 And it's such a cool feeling to work through those things.
10:44 But until you learn the perseverance, you just think, well, I wasn't good at math.
10:49 I must not be good at programming.
10:50 I'm out.
10:50 Yeah.
10:50 I think that keeps a lot from a lot of children to learn or to like learning things that are
10:55 hard.
10:56 Lots of kids struggle with math and yes, like STEM classes.
11:00 But I think it's often because they feel like I don't understand this might also not be explained
11:06 in the best way, but they just shut down and say, okay, I'm just not going to try.
11:10 And if you understand and maybe also, I know that there's this huge psychological research
11:16 on growth mindset that you understand that you shouldn't praise just an outcome, but rather
11:24 the effort that kids try to do something.
11:27 They try to improve and put in the work that that's just so much more important than reaching
11:32 the goal in the end.
11:33 Yeah.
11:33 Yeah.
11:34 We can really help our kids to become more robust and more joyful about learning by
11:40 teaching these principles, for example, through learning how to code.
11:45 This portion of Talk By The Namedy is brought to you by WorkOS.
11:48 If you're building a B2B SaaS app, at some point, your customers will start asking for
11:53 enterprise features like SAML authentication, skim provisioning, autologs, and fine-grained
11:59 authorization.
11:59 That's where WorkOS comes in with easy to use APIs that'll help you ship enterprise features
12:04 on day one without slowing down your core product development.
12:08 Today, some of the fastest growing startups in the world are powered by WorkOS, including
12:14 ones you probably know, like Perplexity, Vercel, and Webflow.
12:17 WorkOS also provides a generous free tier of up to 1 million monthly active users for AuthKit,
12:23 making it the perfect authentication layer for growing companies.
12:26 It comes standard with useful features like RBAC, MFA, and bot protection.
12:32 If you're currently looking to build SSO for your first enterprise customer, you should consider
12:37 using WorkOS.
12:38 Integrate in minutes and start shipping enterprise plans today.
12:42 Just visit talkpython.fm/workOS.
12:45 The link is in your podcast player show notes.
12:47 Thank you to WorkOS for supporting the show.
12:49 Now, you did give this as this topic as a talk at PyData.
12:56 Was that PyData Berlin?
12:57 Where was it?
12:57 And I gave it once at PyData London and at PyCon Berlin and at Europy.
13:03 Okay.
13:03 Yeah.
13:04 So the reason I was going to bring that up is you had some really cool pictures.
13:08 Yeah, I know.
13:09 You'd come up with and like a little persistent kid working away there and stuff like that,
13:15 right?
13:15 Oh, I loved them.
13:16 I loved creating them.
13:17 I used Deli 3 to create them.
13:20 And I spent so much time just playing around with a model and providing it prompts to see
13:24 which images I liked best.
13:26 Of course, there were the obvious problems with some of them that the kids had six fingers
13:30 and so on.
13:31 But still, it was amazing to create these images.
13:35 And I loved the Perseverance one.
13:37 And we can link the article to my blog later where you can see the image.
13:41 It's just everyone laughs when they see the picture.
13:44 Yeah, the pictures are great.
13:45 The pictures are great.
13:46 All right.
13:46 Let's talk for a minute about brain development and maybe the different stages that kids go
13:52 through because there's kind of four or five stages, which then you might map over to the
13:57 different types of resources that we're going to talk about.
13:59 Yeah, I think that's a really important topic to consider.
14:01 If you want to understand when your child is able to do certain things, then you need to
14:06 be able to understand how their brain develops because our brain matures over time.
14:11 It's not fully mature at birth, but quite the opposite.
14:15 And some regions of the brain take more time to develop and some like vision and hearing are
14:20 quite well developed already at birth.
14:22 So at certain ages, it does make sense to start coding, for example, from zero to four.
14:29 And there is not much there for them to really have the cognitive abilities to understand
14:35 computational principles or really sit down and concentrate and focus.
14:40 Yeah, for example, at birth, you have quite a lot of neurons already, but just 25% of the
14:46 adult size brain.
14:46 And when you reach the age of four, you already have 80%.
14:49 So it has grown a lot through the first four years.
14:53 And you do have a lot of influence as a parent or caregiver, friend, whatever.
14:57 Mostly the primitive areas of the brain develop first, like hearing, vision, emotional regulation
15:04 starts developing, but really cognitive and executive functions like planning and so on come later.
15:10 So I guess zero to four years would be or birth would be the first stage.
15:14 And then zero to four years where you have lots of things happening and you can influence that
15:20 by positive influences from like responsive caregiving, that you have diverse learning experiences and
15:28 playing with a child. And then at four years, it gets starts getting interesting. And that's also
15:33 where you can start doing things with your kid. Like, do you want to rather talk about the
15:40 development first and then about...
15:42 Maybe we should talk about the resources that go with each stage. What do you think?
15:45 Yeah.
15:45 Yeah, let's do that. So yeah, I do too.
15:47 Since we already reached age four now. Oh yeah, nice. Yeah. So at age four, you can teach basic
15:53 algorithmic thinking. You can ask questions like, what would you do to guide a lost puppy home? Just
15:58 making them start to think about how to break down problems into smaller steps. But also they have
16:05 the motor skills at that age and the perceptual abilities to interact with simple toys that teach
16:11 the basics of coding. And you open the BeeBot, which is a tiny floor robot, or I guess it's not so
16:17 tiny. It's a Bee and it has four directions to go. Front, back, right, left. I think it can remember
16:23 up to 130 commands and you can press go and program the way it's supposed to crawl or walk, however you
16:31 want to phrase it.
16:32 Yeah. So one thing you might do with this thing is... So this is a little robot that has wheels.
16:37 It looks like a Bee. What you do is you push the buttons like forward, forward, right, forward,
16:42 left, forward, forward. And you might put out something on the ground, like a little
16:46 like, can you make your Bee go around this thing and then through this little gate or whatever,
16:53 right? Those kinds of challenges.
16:54 I think even when you purchase them, you can purchase rucks that have certain paths on them
17:00 and so on. I guess it's a very...
17:02 Right.
17:02 You can spend a lot of money on these kinds of toys. But maybe as a side note, if you start looking,
17:09 you will find tons of robots in different price ranges. So I guess we will only mention examples.
17:15 But if you start looking, you will definitely find lots of different options.
17:20 Yeah. Yeah, absolutely. Would you say that this RoboTurtles game falls into the same category?
17:25 Or is that a little bit older?
17:27 Oh, I'm not sure from the top of my head if it's older. What I like about it is that it's a board
17:31 game. So that's... I'm always asked about screen-free offers. So something that you can play
17:36 without sitting in front of the laptop because screen time is just a general huge discussion
17:42 point. I would have to look up.
17:44 So if I... Yeah, looking at the box here, it says ages four and up. So probably.
17:48 Oh, nice. That's really cool. Yeah.
17:49 Yeah. So this one is... I think it's almost exactly the same problem. There's a little bit
17:54 more to it because there's a couple of challenges in the board game. So I think we actually have this
17:59 board game from when my daughter was young. And you have a little turtle, which is a card and a board,
18:04 and you can put stuff on the board like little rocks. It's... It can't go through. Maybe there's
18:09 like an ice wall and it has ability to like melt the ice, but it has to do that before it can move
18:14 forward. You know, so you get a bunch of cards and you put them in a stack and then you like
18:18 play them out to see if your turtle wins the game or something like that. So this is another
18:23 pretty good option at that age, especially if you want something not electronic.
18:26 What I also like about it is that it becomes a family activity that you learn. That's just in
18:31 general, a very good thing if you want to teach your kids how to code, that you make learning a fun
18:36 activity and playing games, being with them, showing interest and yeah, having fun doing it
18:42 like as part of gaming or what you do at home, playing board games. That's just a very easy way
18:48 then to get started and to get them interesting. I should point out like the actual Robot Turtles
18:52 website has a bad SSL certificate right now. So I'm sure you can find it on like Amazon and other places,
18:59 but it's... Yeah, I'm sure. Okay. So what else? Another one you talked about is Cubelets,
19:05 but this field, I guess, might be a little bit older. Cubelets, it's... Well, you can start
19:09 early with them, but you can also use them at a later stage because you can program them using
19:14 visual coding languages or one of them may code, but you can start quite early. These like Cubelets
19:21 are small physical blocks. As you can see there that you just plug together and some of them move,
19:27 some have cameras or sensors, and you can build lots of cool, unique robots with them. And if you start
19:33 looking at demos on YouTube, it's really amazing how cool they can look, the end robot. I think one
19:40 disadvantage of this is that it's quite expensive. So one of these blocks is about 50 euros or maybe
19:46 $45, $50. So if you want to build big robots and have lots of options, then you need to invest quite a
19:54 bit of money.
19:54 Yeah. I like that the website says free shipping on orders over 50. It's like,
19:58 okay, pretty much anything. It sounds like.
20:01 Yeah, I guess. But I still, I still, I love it because it makes you like be creative,
20:07 especially having this aspect that you can program them later on using MakeCode. That's one of the
20:12 visual programming language. I think that's the run for Microsoft. You can keep using them over a long
20:17 period of time.
20:18 Yeah. For maybe a mental model for people who haven't seen these in action, because even look
20:23 in the website, you don't know, like, what do I do with these things again? Why are they here? I feel
20:27 like they should have maybe a little animation or something, but there's these cubes as the name
20:32 would imply, but they're almost like Lego blocks that each block is programmable. And then you combine
20:38 them into a thing that does stuff, right?
20:40 I think you explained it well.
20:42 Yeah. Thanks. So I think that that's pretty interesting, but this is probably in the next stage,
20:47 right? The next stage would be maybe six to nine. What do you think?
20:50 Yeah, exactly. I think the next stage regarding development would be around six to nine. Of course,
20:55 you also always have to mention it's, this is now for normally developing children. It's just an
21:01 average. Every child is different. So if you observe your child, you know, which skills develop at what
21:07 point and what might be easier for them, what is harder. So this is not like hard ranges, but yeah,
21:12 if you start with about six years of age, you can start using visual programming tools because kids
21:19 become more used to using technology. They have a better hand eye coordination. And also one very
21:25 important part of the brain, the prefrontal cortex, it's like the CEO of our brain, has a big growth spurt
21:31 between five and eight. And this improves working memory, planning, attention, and all kinds of mechanisms
21:37 that you need to start really sitting down and code. And you already opened Scratch Junior.
21:43 Yeah. And Scratch Junior is, I think Scratch is quite popular, one of the most popular visual coding
21:50 languages. And Scratch Junior is just a simplified version of it for very young children starting at
21:56 five to seven. So it has no text, but rather actions like movement. And visual programming in general,
22:06 you have puzzle pieces to represent concepts like loops usually, or I don't know, variables,
22:12 logical expressions, and you can plug them together. So you don't have to worry about syntax or using the
22:18 command line. You just create these programs by putting together puzzle pieces. So that's,
22:24 and that happens on a visual interface. So that's what visual programming is about.
22:29 And Scratch Junior is just a very simple version. I think it's just a free app you can play on tablet
22:36 and create little programs where the characters move around and do things.
22:40 Kind of like the bee, but you more look a little closer to real programming, but then you see the output,
22:46 right?
22:46 Yeah. And you start really using, I guess, these plug-in principles that you have the blocks that you put
22:52 together. So when you go on to, for example, Scratch or another of the visual programming languages,
22:57 you're already, you have knowledge about how it works in general, I guess.
23:01 As I look at this website, I was thinking, you know, when I think about coding, I think about
23:06 computers, Mac, Windows, whatever, with apps. But obviously, young kids are way more in tune with
23:14 touch devices like iPads and Android tablets and stuff, right?
23:17 It's amazing how quickly they adapt and learn it. I think it's quite, sometimes I'm blown away by how
23:23 young children can already understand how to swipe and select stuff on a touch screen.
23:28 I think actually it probably lowers the age by quite a bit that kids are able to do this kind of stuff
23:34 because these touch interfaces exist in decent ways.
23:37 Yeah, absolutely. Just learning how to type is actually one of the main reasons why you can
23:42 only start with textual programming later because typing is hard. You need to learn how to do it.
23:48 Just touching and dragging and dropping is much easier.
23:51 When my older kids were very young, we wanted to have them work with things like this and just
23:57 learn how to use computers. And they, this predated the iPhone, like it didn't exist.
24:01 There was no meaningful touch screens that really you would want to use. And so we got like, kind of like you get a
24:07 typing program to learn to touch type. We got a mousing program and there was like a little airplane and they
24:13 had to like chase the airplane around with the mouse to learn how the eye hand coordination of mouse and then like
24:18 screen, right? When you're three or four years old, like that's not natural, right? But touching, they already be all over that.
24:25 I think sometimes it's even too intuitive for them that it starts having like having a very huge influence
24:33 on them way too early, but I guess that's a different discussion.
24:36 Yeah, that's a different problem. That sends you back to a robot turtle board game.
24:40 Yeah, exactly.
24:41 This portion of Talk Python To Me is brought to you by us. I mentioned at the top of the show that we have a
24:48 wide range of courses focusing on core topics such as getting started with Python and advanced ones like
24:54 APIs, async programming, and deep diving into Python's memory management and more. But did you know that
25:01 we have a set of world-class apps that you can use in addition to our web platform for taking our courses?
25:06 If you're using a tablet or even a phone, apps are clearly the best option, but there are other
25:11 reasons to check them out as well at talkpython.fm/apps. Our mobile apps offer offline playback,
25:18 which allows you to download portions or even complete courses. We hear from users who learn on the
25:24 way to work on the subway, where connectivity is tricky, as well as to those who have secure
25:29 environments that don't allow them to connect personal devices or which have limited connectivity.
25:34 And even though I've done a ton of work to make our video delivery excellent, no matter your location
25:39 in the world, there are still places with very slow internet. Downloading a course and then watching
25:45 it without pauses is a really great use case as well. The app is 100% free and it includes eight free
25:51 courses that are a single tap away. So give it a try at talkpython.fm/apps. Now back to the show.
25:58 A little bit later, we could do, once you start doing this, some kind of programming language,
26:04 then that opens up a bunch of resources, right? So obviously Scratch is sort of the way more full
26:10 featured version of Scratch and Junior. That's pretty neat.
26:14 Yeah, I think Scratch is amazing because I think for kids, it's great. I know lots of adults that still
26:19 use it for some projects where you really want to make it come alive because Scratch is focused on
26:25 having really cool, interactive, fun projects. They have sounds, music, you can add graphics, and it just
26:35 offers a lot of functionality to create your project, share them with friends. And there is a ton of
26:41 resources on learning Scratch. And as you can see here, like make music, create a story, create a
26:48 character. I guess your possibilities are endless. Yeah, it looks really, actually, I didn't realize all
26:53 the stuff they got going on here. They have a bunch of tutorials, free coding community. Super cool.
26:58 Then I guess just while we're talking on these visual programming languages, we could talk about
27:02 Blockly, right? Yeah. When I, like I knew Blockly existed, it was also free, like Scratch is also
27:08 free. I guess that's important to mention. And Blockly is actually at the basis of most of the
27:14 other visual languages. For example, it is actually like block-based languages like Scratch and MakeCode
27:20 are based on Blockly. Blockly is developed by Google. And with Blockly, it's, I think it's for a bit older
27:26 kids because it's more low level. If you can say that, it offers you more flexibility.
27:31 You see the code next to the blocks. You see it in an editor, how it actually looks like,
27:37 and you could copy-paste the code into like a normal editor and run it. It's more low level,
27:44 but also somewhat more sophisticated, the editor that you have it more, it looks more like coding
27:50 to me than Scratch.
27:51 Maybe the way to think about it, you see this more low level. I would say each block almost
27:56 corresponds to a single symbol of code, almost, right? Like you have a set variable too, then you
28:04 put another block on, which is the value. And then, you know, you've got your visual editor,
28:08 but then side by side, you have your JavaScript, or I imagine you could probably see Python or other
28:13 languages if you, there's a dropdown for choosing the output language.
28:16 Yeah. You can use JavaScript, Python, PHP, Lua, or Dart.
28:20 Yeah. So that's kind of getting a little farther up there. And maybe we could talk
28:23 a bit about the hardware side, because that's one way that it actually can be something you can touch
28:29 and feel. And as you interact with these ideas, right?
28:31 I know that that's nothing I ever used, but my brother started using it. Like I know that he
28:36 bought a Raspberry Pi. You open now the microbit, which is like a smaller programmable device.
28:42 And the Raspberry Pi would be like full-fledged computer in a tiny device. But yeah, you can
28:47 learn a lot about hardware and also coding by having such devices. And the microbit has displays,
28:54 buttons, sensors, and you can program it using MakeCode, one of the other visual programming
28:59 languages. And I think it's quite cheap compared to other devices. Like a Raspberry Pi is, I think it's
29:05 not expensive for having all these abilities or these capabilities, but the microbit is, I guess,
29:12 more affordable for lots of people. Oh yeah, nice. There you can see how it works.
29:16 And you know what's really interesting is if you go to makecode.microbit.org, even if you don't have
29:22 one of these devices, it comes with a little emulator and then it has a virtual microbit that you can write
29:29 code against. And it gives you an option as well to choose Python or Blockly or some other way of
29:36 working with it, which is pretty cool. Exactly. That's also why it's recommended for children,
29:41 like officially it's recommended for children at the age of eight or older. And Blockly, I think,
29:46 is even recommended for kids starting at 10, whereas Scratch is for even younger children, right? They say
29:52 you can get started at eight. And they say what I think, which is funny, they say it's up to 16,
29:57 which doesn't make sense to me. Why would there be an upper limit? But yeah, anyway, you can still
30:03 use it. You have to do C++ now. Yes, exactly. What is great about visual programming is that you can
30:08 always come back to it. It's not that you progress from these robots to visual programming to textual
30:14 programming, but you can use visual programming for doing, I don't know, digital stories and you can
30:20 still do textual programming at work. It's just having all these options now is really nice. Yeah,
30:25 absolutely. Let's see. We also have Zumi. Zumi is pretty cool. Let's come back to Zumi. I do want
30:30 to talk about something that's like a little bit more real similar to the micro bit first is many of
30:35 the things over at Adafruit. Are you a fan of Adafruit? I don't know Adafruit. Tell me about it. So this is a
30:41 company that creates a whole bunch of small devices like the BBC micro bit that run CircuitPython. There's
30:49 just tons and tons of things you can buy. You can buy little sensors and you can buy little
30:55 displays or whatever it is that you're looking for. And there's just many, many little ways to make
31:00 these projects a little bit more than a micro bit. So for example, you could get one of these ESP32
31:06 devices, but it has like a little tiny display on it that you can output your text to. And it costs
31:13 $19, which is pretty ridiculous. And they often come with tutorials on how to do it. So if you're
31:20 into this kind of stuff, this is like a perfect place to go look.
31:24 Also, there's just so much opportunity to learn, even for like being the parent, I would learn so
31:29 much from doing this. It would be so valuable to me to learn more about the hardware side of things,
31:36 especially because I would never sit down and buy myself a Raspberry Pi. I don't know why,
31:41 but I wouldn't do it. Just don't find the time. But if I can do it...
31:45 You already have a computer and all that.
31:46 Yeah. And if I can do it together with my children, I think that's just amazing. It's really cool.
31:51 This is just a general thing about learning with kids. If you learn together with them,
31:56 they can also be the expert sometimes, which is amazing for kids. If they can explain something
32:01 to you that they understand better, it gives them so much joy and helps them develop this passion and
32:08 love for learning. I think that's a great thing about learning how to code that doesn't matter if
32:13 you are the best coder, but you can just use it as a way to improve yourself.
32:18 Yeah. And once they get that mastery, they're like, oh, now I've gone beyond them. It's probably a
32:23 really good feeling.
32:24 If my kids want to learn how to code early, like much earlier than myself, they will become so much
32:31 better than me so quickly.
32:32 Yeah, for sure. I have one of these little devices here. You put it in your hand. It's
32:37 certainly smaller than the palm of my hand. And this thing manages the DNS and ad blocking on my
32:43 network. It was like 20 bucks or something. Yeah. There's sort of less playful, more interesting.
32:49 Also just, you know, utilitarian things you can do with these little things.
32:52 Yeah, absolutely.
32:53 All right. Back to Zoomy, which is in the same age category, I would say. This is like around 10 years
32:58 or so. Yeah.
32:58 But it's more robot-like, right?
33:00 Yeah, exactly. Like it's a self-driving car kit. Like it's a small car and it has so many
33:06 capabilities. You can program it using Python and Blockly. You can even teach it about driving
33:12 certain ways by providing your own data sets. So there is a lot of machine learning. Even you can
33:18 teach it. It offers so many capabilities or ways to create projects. At my company, we have done quite
33:26 a few workshops with kids with Zoomy and they love doing it. And adults love doing it too.
33:31 Nice. It's like a self-driving car kit. So if you wanted to try to, instead of maybe teaching it,
33:38 you go forward three steps, you turn right, you go forward two steps, you turn left, you teach it.
33:42 If you see a turn left sign, you turn left or something like that, right?
33:46 Exactly. Yeah. It can really understand or analyze its environment.
33:50 Yeah. That's pretty awesome. Okay. And you do events with these?
33:53 Yes. That's also maybe advice for people that want to get started. It's always useful to check
33:59 out local events that happen at companies that are close to where you live or universities. They do
34:05 offer a lot of free, often offer free workshops for kids where you can sign them up to learn about
34:10 robotics or coding. And it's can be like an easy way to get them started if you find it hard to do it
34:18 yourself. Yeah. I think a lot, at least in the U S there's quite a few programs for like summer teen
34:24 programs that do like either 3d printing or, you know, coding with, you know, Lego robots or whatever.
34:31 So there's a lot of summer camps and that type of things.
34:33 Yeah. I guess that's very big in the U S and Germany. I think not so much, maybe it's growing,
34:39 but yeah, you can definitely spend a lot of time doing it. And I know that like we at our company,
34:46 we sometimes offer day workshops where you can just start getting to know about a topic or just play
34:53 around with things, becoming kids interested in the topic in the first place.
34:57 Yeah. That's really neat. Last in the category of hardware here, you already mentioned it though,
35:02 is a Raspberry Pi, which I guess is a little closer to just a real computer, right?
35:07 Yeah. It's a really powerful device. So it's basically a very small and cheap computer that
35:13 runs Linux, but you can use it to learn coding, but you can also build hardware projects with it,
35:19 do home automation, learn about the internet of things, but it's recommended for kids starting at 11
35:25 years. So quite a bit older because you need programming. This maybe also shifts over to the
35:30 next age range, namely when your kids have typing skills and also a more well-developed cognitive
35:37 abilities and the prefrontal cortex, which I talked about the CEO of the brain, the development starts
35:44 to mature and stabilize. So planning, organizing, thinking abstractly, all these skills become more
35:50 fully developed. And you of course need the typing skills to get started with textual coding.
35:55 So at the age nine plus, most of the time you can get started with these things, for example,
36:01 with like programming Raspberry Pi or just more traditional textual programming languages.
36:08 The typing skills is pretty, pretty interesting. I think one that I, you talked about before,
36:13 but I think is also super interesting as a gateway to this. This is the best one that I know. Maybe
36:19 people know of others as well is code combat.
36:22 You did a podcast episode on that years ago, right?
36:26 This is one of the ones, like my daughter and I both subscribed to this for a while when she was
36:31 younger. We'd go through and we did, I don't know, like, can't remember. I think she did 30 or 40
36:35 code challenges through there or something like that, which was pretty awesome. And I also had the
36:40 guys on the show. Yeah. It's been a little while.
36:42 Yeah, it has been, but it's still, I think it's an amazing resource. So you, a code combat is about
36:46 learning how to code through gaming. So you play a game from beginning to end. And while you play the
36:52 game, you learn to code in Python or JavaScript. I think there are several languages, but you really
36:57 do textual programming. And if your kid likes gaming, or this is something that makes it easier for them to
37:03 get started with coding, it's an amazing resource, even though you have to pay for it because you're
37:08 really guided through the course. You can have lessons. You can even have, I think, teacher
37:13 lessons once or twice a week, dependent on your subscription plan.
37:17 Yeah. I think there might be a free tier if you tell it you're a student, but you can only do certain
37:22 challenges. Like for example, see this, there's like a locks here and it says, I think, yeah, I have to
37:28 subscribe to this if I want to do all, if I want to solve all the puzzles, but there's some of them you
37:33 can do for free, I believe. I don't feel like we had to pay at the beginning, but they could have
37:37 changed the model. I also played around with it. At least in the beginning, you can try it out for free.
37:42 What I really like about this, you know, so if you click on, if you go to this, you click on the things,
37:46 it says for this challenge, you're going to learn arguments and syntax. Or if you come over here and you
37:52 click on this one, it'll say you'll learn while loops or whatever, but then it gives you just a nice
37:57 simple challenge. So it, but what's cool, I'll know in order to play that one, I got to, can I play this one?
38:03 Yeah, here you go. So you have this character and what's, oh my gosh, it made that very large.
38:09 What's really cool though, is when you, it gives you a little hint, but the editor, here's what I
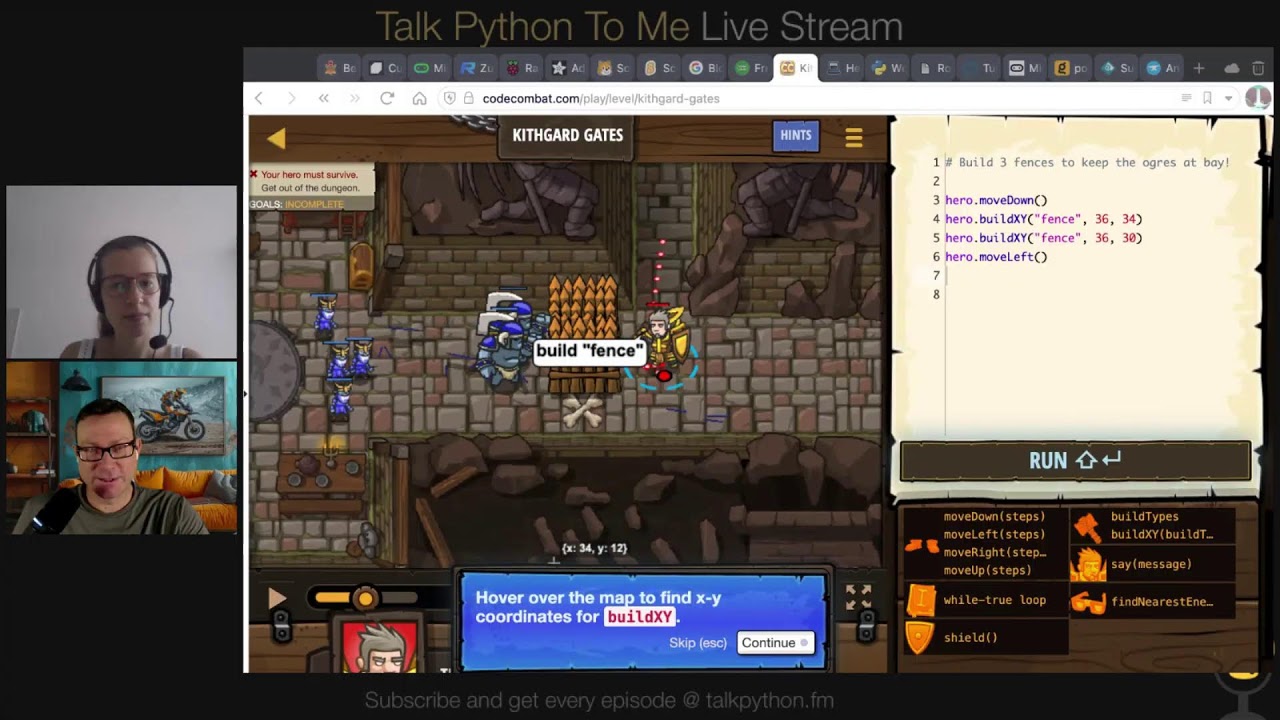
38:14 think is special about Code Combat. The editor is auto-complete like you have never seen.
38:19 You know what I mean? So it says, all right, what you need to do is build a fence and you have a hero
38:24 and the hero has the ability to say build at X, Y position, or it could move. And if I just type the
38:31 letter D, it'll auto-complete like hero dot move down. Or if I say hero build X, Y, it automatically
38:39 puts in all the, it's, so if you can type just a couple of characters, it'll keep the syntax, you know,
38:44 like the spacing for indentation and block definitions. And all of that kind of stuff is
38:50 ridiculous for how you don't even have to really have the right syntax. You just have to put a little
38:56 bit of some kind of word in there at all. And it'll, it'll start to write all of it for you, which I
39:02 think that's the magic here.
39:03 It's nice that you have this insider knowledge by having tried it out yourself for quite a while.
39:08 Yeah. It worked way better than other stuff when my daughter was young and I was trying to teach her
39:13 like beyond the visual programming things, but it's, it's so forgiving compared to, well, here's your
39:19 favorite editor and you start typing. Oh, why won't it run? There's three spaces, not four. Oh, I see.
39:24 You know, all that kind of detail you got to normally deal with.
39:27 It can be so frustrating in the beginning. If you need to learn about everything at the same time,
39:31 like syntax, spacing, brackets, it's just a lot to learn in the beginning. If you just want to
39:37 understand the basic concept and like for a start.
39:39 Yeah, absolutely. Another thing you put out there was code club.
39:43 Yeah. That's, I think a really cool resource by the Raspberry Pi foundation. So it's a platform and
39:50 it guides your kids from lesson to lesson. So you start with learning scratch, but then it progresses
39:58 onto Python and yeah, you can start, I think at the age of eight, yeah, you can start at the age of eight,
40:05 which is also the recommended age for scratch. And this is just an example for a full platform that
40:12 you can use to guide yourself or your children through progressing from one thing to the other.
40:18 And I think it's also free. So if you start looking, there are lots of online coding classes that you can
40:24 use that teach you different things and have a whole program and sets of ideas behind how to approach
40:31 different topics.
40:32 Yeah. This looks very fun. And the example, at least they have on the screen is using Blockly, right?
40:37 Or scratch one of them.
40:38 I think it's scratch. Yeah. I think level one is scratch and then level two would be Python and more comes after that.
40:44 Yeah. Oh, that's really cool. Another one in this realm is Hedy. I had not heard of Hedy.
40:49 Yeah. Me neither. Just when I started researching the topic, why I chose it as an example is that I just like the concept of
40:58 gradual programming. So gradual programming means that what I just mentioned, basically, that if you learn language,
41:04 speaking or like a programming language, you have to learn a lot at the same time. It can be overwhelming.
41:11 You have concepts like loops, if else, and syntax like quotation marks, round brackets.
41:17 And in Hedy, it's free, like it's a web-based interface. And concepts are introduced with as little syntax and then refined.
41:26 So in the beginning, you can just type print and the text. And you don't have to worry about quotation marks or brackets.
41:33 It's just introduced at a later stage. So it mimics the way in which we would learn a language.
41:37 And in the end, you like it's based on Python. So you learn a subset of Python, not the entire programming language,
41:44 but it's syntactically valid and you have all the right syntax. But for some kids, it might be easier to get started with
41:51 having not everything like being part of what you have to quote yourself.
41:55 Right. Like learning, oh, whoops, you forgot to close the parentheses.
41:58 So it's not going to run or you forgot to close the quote. So it won't work. Something like that.
42:02 Yeah, exactly.
42:03 Yeah. Kids run into that all the time because they're like, well, I see the words on the screen that I wanted to do,
42:08 but no, no, you got to put it in quotes. And why?
42:11 Oh, and maybe regarding the age, this is recommended for age 10 plus years. So yeah, when you want to get started with
42:17 actual textual programming. So it fits into the third age range that we discussed.
42:22 That's pretty much the last limited age range, I guess you would say before you just go and do regular programming, right?
42:29 Exactly. From there, you can just progress on to more traditional programming languages.
42:33 There are lots of resources like from the Bersbury Pi Foundation. They have Python courses and there are some on Udemy.
42:40 If you start looking, there are tons of resources to get started.
42:44 There are lots of online and on-site classes that teach kids starting at various ages.
42:50 Yeah, I know about a few German offers where you can really find what you're interested in,
42:57 which is really important, like make coding fun and learning fun for kids.
43:03 So find out what they are interested in, what their passion is, and then find something that fits their interest.
43:09 I'm sure there's a ton of stuff on YouTube as well to help people, but at least I'm out of touch.
43:15 I bet there's a lot on TikTok actually.
43:17 Oh yeah, I'm out of touch with that as well.
43:19 Just, you know, you learn one concept every 30 seconds. You just swipe away until you're a programmer.
43:25 I should actually look at that probably when talking about coding with kids. I guess that's something that can play a big part.
43:32 For sure. Instagram reels or whatever. I think that kind of touches on most of the resources that we have out there.
43:39 There's one more I do want to talk about though. And I think this is probably as good around, it's beyond the code combat stage where kids can actually use an editor to create proper valid syntax.
43:54 But it's not much beyond that. And that's Anvil at Anvil.Works. Are you familiar with Anvil?
43:59 No.
43:59 So I've had Meredith create this online on the show. But what's really interesting is it's a way to visually build webpages that are actual real webpages that people can actually, you know, you publish it, your family or your friends could use it.
44:17 So if you wanted to build, you know, something like a Harry Potter type thing and you could have your friends vote on which one, which character is their favorite and why or whatever, you know, like you could build this into a web page and publish it.
44:29 And with so many of these projects, it's like, okay, I built this cool thing. How do I share it? Or how do I make it look like the thing that I use?
44:37 And so you can do this drag and drop, build it out thing. But then you write the front end, the front end interactive code in Python and true Python JavaScript.
44:46 And then it has kind of like a simplified database in the backend. So it was like a little bit of like persistence and storage, but it's, it's really cool.
44:54 After we did code combat with my daughter, we went and we did this and she built a bunch of things that were like really, she really thought were pretty neat.
45:02 She could share with people and have people input little text messages or whatever.
45:07 I love that. Yeah. I would learn again. I know very, I have very little knowledge about web programming.
45:13 This would be a good tool for me to get started as well.
45:16 Yeah. Well, also the problem is even if you're a very good web programmer, it's like, okay, kid, you go from code combat to now you're doing CSS, HTML, database, you know,
45:29 like the explosion of complexity to put, and then you do all that. And then how do you even put it on the web?
45:34 It's just so out of control that step from one to the next. And so if people want to do anything with like web pages and Python, this is a really cool option.
45:42 I think right here.
45:43 Really cool. Yeah. And like speaking from your experience, how did you get your kids excited about coding? Did they just like it or do they hate it?
45:53 My older daughters, they grew up with less technology because they're older. So at first they weren't super into it, but then they got into college and they had to start learning things for their degree.
46:05 And so now one of my daughters is doing a lot with R, which is fine because she's in psychology and that's what all of her colleagues are using.
46:12 Which is fine. It's not ideal, but it's fine.
46:16 It's not ideal. It's fine. No, I'm not that. No, I'm very proud of her.
46:20 I think there's different things that can motivate you. You know, you can just be curious. Like my youngest daughter is like, let's play games. Let's play code combat.
46:28 Then she's like, I want to build something for my friend, you know, and so we did this thing with Anwell and she was very motivated, like seek out the technology and play with it.
46:36 Whereas my older daughters, I think they, they weren't that interested and they had other things to do, but once they got somewhere with a job or with their education where they needed it, then all of a sudden it was more interesting.
46:47 So, you know, it varies by kid, I think.
46:49 Yeah, absolutely. And I guess that's fine as well. Not everyone needs to like coding, but just having the opportunity to learn about it and experience yourself if it's something that you're actually like.
47:00 I was just so blown away when I experienced how fun it is to learn how to code.
47:05 I always thought it was boring and having all these stereotypes in my head because I never actually knew anyone that was coding.
47:15 It's nice that they had the opportunity to learn about it at home.
47:18 Yeah, it absolutely is. So I think we have a little more follow-up here on the TikTok learning style.
47:24 Ty Vass Heather says, you can learn every single short, but you won't remember anything as you flip through them.
47:30 Flip, flip, flip, which is probably true.
47:32 And then also, Krishan asks, you know, do you think Scratch is good to start with for kids?
47:37 Like if you had a kid who was 10, 11, 12, 13, what would you start them with?
47:42 Yeah, I would get started with visual programming. I think it makes it easier.
47:45 I know that for some kids, it can be hard then to progress onto textual programming.
47:49 But I guess this is just a general thing. You need to see what works.
47:53 It's not that you, it might be that you start with one thing and you see, actually, it doesn't work for us.
47:59 And then you have to switch tracks. And that will happen a lot. And that's just fine.
48:03 You need to find your own path through it.
48:05 And don't be afraid to actually make changes if you are not enjoying what your kid is not enjoying their work.
48:12 I think visual programming is a great and fun way to get started with coding concepts and not have it feel like you're actually coding.
48:21 Absolutely. So, Christian's child is 13. I will consider code combat, actually.
48:26 I think, you know, 13, you're well enough to do textual stuff if it's not too much drudgery, right?
48:32 Like matching braces and quotes and all that.
48:35 So maybe if this kind of thing inspires, maybe that as well.
48:39 Yeah, absolutely. I think 13 is great for getting started with textual programming as well.
48:43 And what is so nice about having large language models now is that lots of these offers are being translated to various languages.
48:52 And it is becoming much more easy to get started in your native language, which might not be English.
48:58 And then you do not have to learn a language while you learn how to code.
49:02 Yeah, that's also, I think, a huge advantage of the current time.
49:06 That's something that's always been interesting to me is so many of the programming languages are in English,
49:12 but many of the programmers, their first language is not English.
49:17 Yeah.
49:17 And, you know, maybe like your English is perfect, I'm sure.
49:20 You know, forward, while it's no big deal.
49:22 But when you're 10 years old, here, you need to learn a program.
49:25 Well, by the way, it's in a foreign language.
49:27 That's pretty wild, right?
49:28 That's got to be challenging.
49:29 What was your, like, how do you feel about this?
49:31 I mean, you're more in it than I am.
49:33 Yeah, I would always start.
49:34 Like, if you have the chance, then start in the native language of the child.
49:38 And you will definitely find good ways to get started and good offers.
49:42 For example, Scratch, I think, is available in lots of languages.
49:45 70 languages, actually.
49:47 Choose something that keeps the cognitive effort that you need to get started with simpler.
49:53 Because otherwise, you really have to learn two things at the same time.
49:57 Learning a language and learning all these concepts.
49:59 And it can then be overwhelming.
50:02 It's not something that I had to deal with.
50:04 But looking back, I'm like, wow, I was pretty lucky that I didn't have to
50:07 learn what all the keywords meant in addition to just what I was trying to do.
50:11 That's also actually why I decided to study in English.
50:14 Because I knew all the papers I'm reading are in English.
50:18 All the code I'm writing is in English.
50:19 It doesn't make sense to study it in German.
50:21 It's just weird.
50:23 The internet has done some interesting things to just sort of spread everything around globally.
50:27 So, all right.
50:28 Anna Lena, this has been awesome.
50:30 A bunch of concrete things for people to take and work with their kids.
50:33 Maybe if they're grandparents, their grandchildren, or if they're teachers or friends, kids or whatever, right?
50:39 Whatever, yeah.
50:40 Yeah.
50:40 How about some final advice to close out the topic?
50:43 Yeah.
50:44 I think for me, two things are the most important ones.
50:47 Namely, first, don't force your child to learn how to code.
50:50 But see if you can find a way that makes it fun for them.
50:54 I think making or learning that learning is actually a cool thing.
51:00 It's like it offers you or it opens you so many doors in your life that you learn that putting in the effort.
51:07 And even if something is complicated, it's worth it.
51:11 It's just one of the most valuable skills you can provide your child with.
51:16 So, yeah.
51:17 Learning how to learn and how to love learning, I guess.
51:20 And there's lots of ways in which you can do it.
51:23 Choose the right topics.
51:25 Be patient.
51:25 Sit down with your kids and learn together.
51:28 Don't force them to sit down for long times and like rather distribute learning sessions over time.
51:35 Don't be afraid to switch tracks.
51:37 Lots of the things that apply to adults also apply to children regarding learning.
51:42 Very good advice.
51:43 I would just maybe reemphasize that people should reward persistence.
51:48 Reward it very, very highly.
51:50 Like, I can't believe you spent half an hour and you just got, barely got it to print hello.
51:54 But that's actually a massive accomplishment.
51:56 And like, I'm so proud of how hard you focused and worked on it, right?
51:59 That's a big deal.
52:00 Yeah.
52:00 That's like, it makes a huge difference to two kids.
52:04 Probably adults as well.
52:05 Yeah.
52:05 Yeah.
52:05 Everyone.
52:06 But you lay the foundation for learning, right?
52:09 So if you...
52:10 Yeah.
52:10 I mean, that expands on to being good at literature or being good at philosophy or like whatever
52:15 it is that's hard to learn.
52:16 And just believing that you can learn anything.
52:19 Yes, exactly.
52:20 And the other is to try to capture inspiration.
52:22 If they're like really, really excited and they really want to learn a thing at that moment,
52:26 then you could introduce some of these tools.
52:28 But if they're like, I want to go outside and play with my French, you're like, no,
52:31 come in here, we're doing coding.
52:32 Like, maybe that's not the moment, yeah?
52:34 Exactly.
52:34 Yeah.
52:35 All right.
52:35 Thank you for taking the time to put this all together and coming on the show and nice
52:39 to have you back.
52:39 So...
52:40 Thank you.
52:40 Yeah.
52:40 Thanks.
52:41 Bye.
52:41 Bye.
52:41 Bye.
52:42 Bye.
52:43 Bye.
52:44 Bye.
52:45 Bye.
52:46 Bye.
52:47 Bye.
52:48 Bye.
52:49 Bye.
52:50 Bye.
52:51 Bye.
52:52 Bye.
52:53 Bye.
52:54 Bye.
52:55 Bye.
52:56 Bye.
52:58 Bye.
52:59 Bye.
53:00 Bye.
53:01 Bye.
53:02 Bye.
53:03 Bye.
53:04 Bye.
53:05 Bye.
53:06 Bye.
53:07 Bye.
53:08 Bye.
53:09 Bye.
53:10 More at talkpython.fm/workos.
53:14 Want to level up your Python?
53:15 We have one of the largest catalogs of Python video courses over at Talk Python.
53:19 Our content ranges from true beginners to deeply advanced topics like memory and async.
53:24 And best of all, there's not a subscription in sight.
53:27 Check it out for yourself at training.talkpython.fm.
53:30 Be sure to subscribe to the show.
53:32 Open your favorite podcast app and search for Python.
53:35 We should be right at the top.
53:37 You can also find the iTunes feed at /itunes, the Google Play feed at /play,
53:41 and the direct RSS feed at /rss on talkpython.fm.
53:46 We're live streaming most of our recordings these days.
53:48 If you want to be part of the show and have your comments featured on the air,
53:52 be sure to subscribe to our YouTube channel at talkpython.fm/youtube.
53:56 This is your host, Michael Kennedy.
53:58 Thanks so much for listening.
54:00 I really appreciate it.
54:01 Now get out there and write some Python code.
54:03 I'll see you next time.